Key Technology - Laser Applications
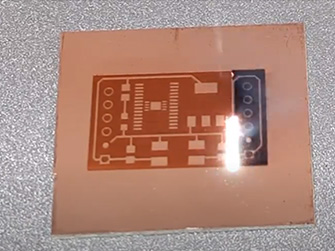
Laser Etching
Laser etching is a broad term that encompasses a variety of engravings and shallow engravings.It can be applied to a wide range of products and materials, including automotive parts, medical devices, wine barrels, microelectronic components, and tombstones.In general, laser etching is distinguished from marking in that it changes the surface roughness of a part, rather than simply changing the surface color or texture.The primary use of laser etching is to create fine patterns, designs, text, images, etc. on a variety of materials, and the technology is widely used in many industries due to its precision, speed, and versatility.
Applicable Materials
- Technical Features
- Material Versatility : Applicable to almost all types of materials, including plastics, metals, glass, and ceramics
- Precision : Precise patterns can be created using laser beamsNon-contact, non-wear processing
- Areas of application
- Automotive parts, medical devices, microelectronics
- Manufacturing precision parts such as electronic devices
- Various metal and plastic parts
- Key variables
- Laser wavelength, power, irradiance, repetition rate, scan pattern, focus position

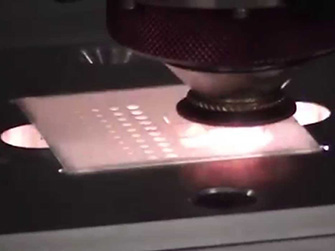

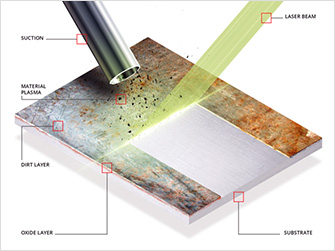
Laser Cleaning
Laser cleaning is a non-contact method that uses high-energy laser beams to remove contaminants from surfaces. The heat delivered melts the material, forming a molten weld pool, which then cools and fuses the target area. This technology is gaining attention as an environmentally friendly and precise alternative to conventional chemical and mechanical cleaning methods in various industries.
Applicable Materials
- Technical Features
- Removal of contaminants by heat : Rapidly heats the surface contaminant layer to vaporize it or peels off the contaminant with gas pressure and shock waves
- Non-contact, non-wear processing : Selectively removes only contaminants without damaging the substrateEnvironmentally friendly, no environmental pollution, no waste
- Areas of application
- Aerospace and automotive industries : parts cleaning, paint removal, maintenance
- Metal surface cleaning : rust, oxides, oil removal
- Heritage preservation : delicate restoration work
- Manufacturing industries : surface preparation before welding and coating
- Key variables
- Pulse width, energy density, scan speed, exposure time, wavelength (typically Fiber 1064 nm)



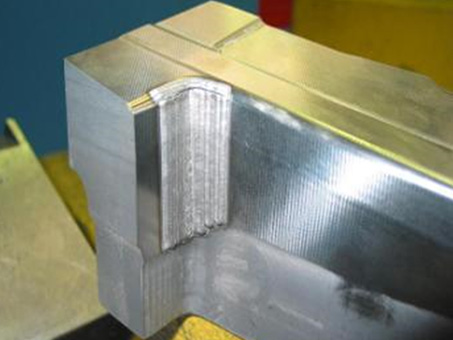
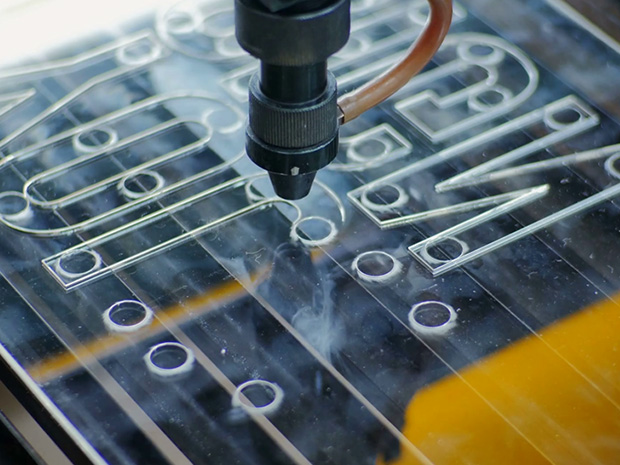
Laser Plastic Cutting
Laser plastic cutting is a technology that uses high-energy laser beams to precisely cut plastics. It minimizes deformation and enables precise processing through non-contact cutting using heat. It is widely used in various industries due to its fast cutting speed and high productivity. It can be applied to various plastic materials and is especially useful when complex shapes and precise designs are required.
Applicable Materials
- Technical Features
- High-speed operation : Increased productivity with processing speeds much faster than mechanical cutting
- Material diversity : Widely applicable to various plastics (acrylic, polycarbonate, polyethylene, etc.)
- Non-contact processing : Processing without physical contact minimizes material damage
- Areas of application
- Display parts, precision parts for medical devices
- Acrylic, film, plastic parts processing
- Cutting, plastic products such as toy/lighting parts
- Key variables
- Output, irradiation speed, focal diameter, processing speed, wavelength (CO₂: 10.6μm, etc.)


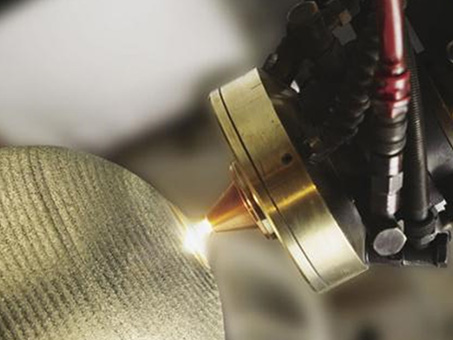
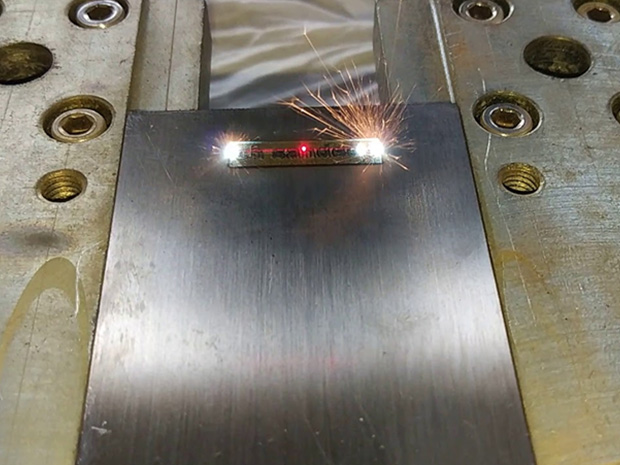
Laser Marking
Laser marking is a technology that uses laser light to change the surface of a material to engrave logos, product names, serial numbers, etc. It can be used to change or carbonize the surface to create clear and durable markings. It is environmentally friendly as it can be applied to various materials without ink or chemicals. It can be applied to various materials and is especially widely used in industries that require precise and durable markings.
Applicable Materials
- Technical Features
- High-precision marking : Precise patterns or characters can be printed in precise locations
- Semi-permanent : Non-erasable and durable, suitable for long-term use
- Applicable to various materials : Applicable to various materials such as metal, plastic, and wood
- High-speed processing : Maximize production efficiency with fast marking speed
- Areas of application
- Automotive parts processing (serial number marking)
- Electronic parts identification code marking
- Medical device logo printing
- Product identification marking for industrial parts, consumer goods, etc.
- Key variables
- Wavelength (Fiber/CO₂/UV), irradiation time, beam diameter, scanning speed, focus position







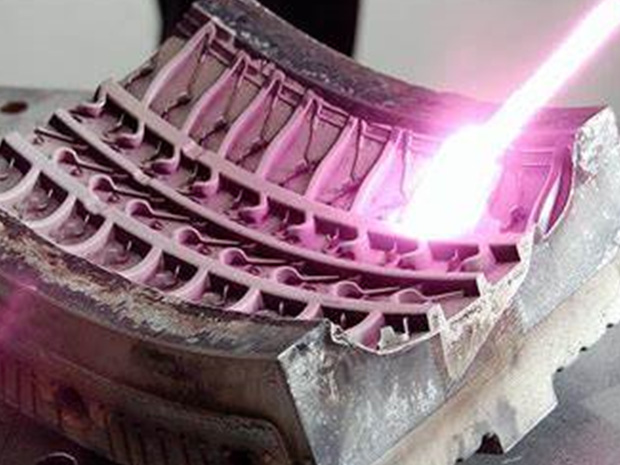
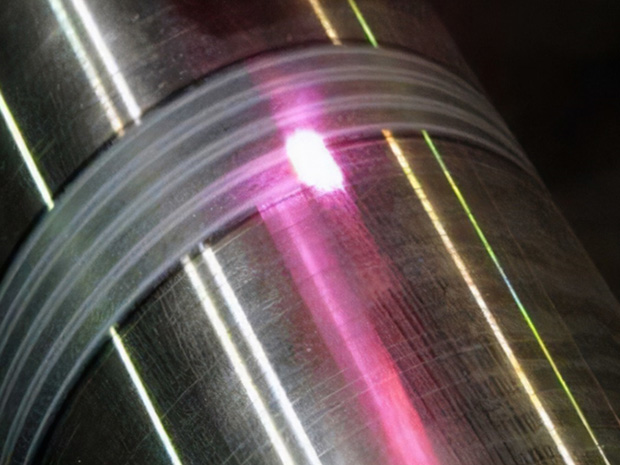
Laser Heat Treatment
Laser heat treatment is a technology that uses high-energy laser beams to locally heat the surface of a material to increase hardness and improve wear resistance. It allows rapid heating and cooling, minimizing deformation, and allows precise heat treatment of individual areas. It is used in various industries to improve the physical and chemical properties of materials.
Applicable Materials
- Technical Features
- Precision heat treatment : Locally focused high energy enables precise heat treatment of only microscopic areas
- High-density energy : Rapidly heats the surface, microstructure control possible
- Improved material performance : Improved mechanical properties such as hardness, toughness, and fatigue strength, and enhanced durability
- Areas of application
- Automotive industry, parts processing
- Aerospace industry, high-strength steel and engine parts durability enhancement
- Metal processing, cutting tools, bearings, mold wear resistance enhancement
- Electronics and electrical industry, surface treatment and improvement of electronic components
- Key variables
- Output, feed rate, beam size, exposure time, cooling rate
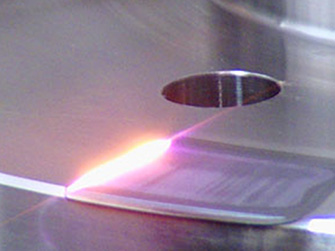

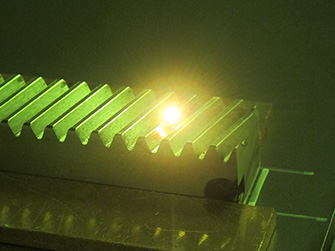
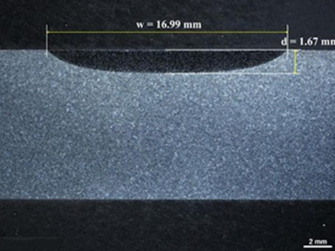
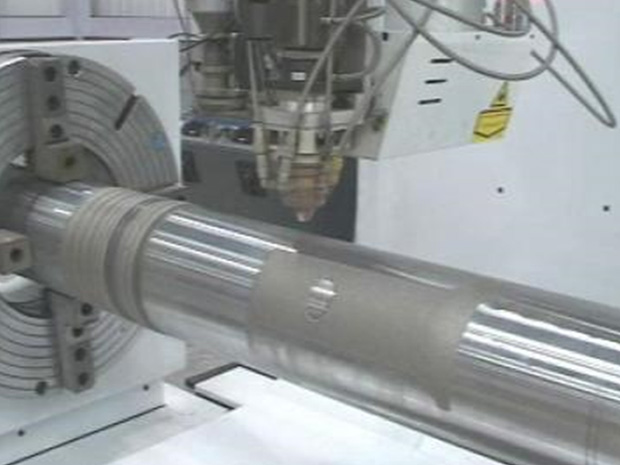
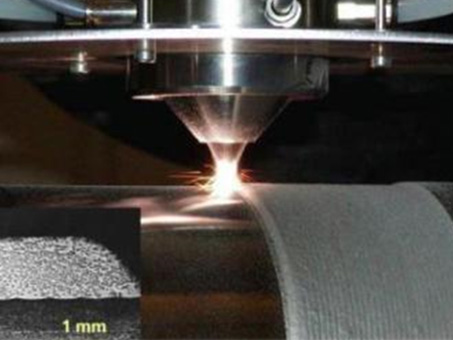
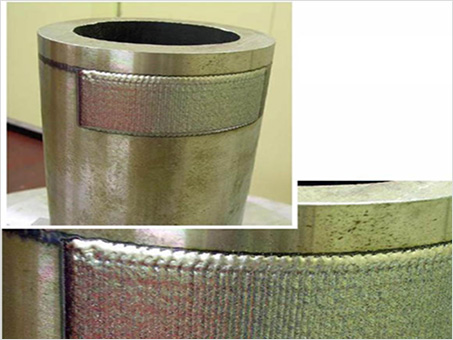
Laser Cladding
Laser cladding is a method of coating metal powder or wire by melting it on the surface of a base material using a laser beam. It is effective in forming a uniform coating layer, giving it stronger properties than existing materials, and extending the life of the part. This technology is widely used in various industries because it improves wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and heat resistance.
Applicable Materials
- Technical Features
- Concentrated heating and rapid cooling : Use concentrated heat to melt the material, and rapid cooling to form a strong metal bond and microstructure
- Minimized heat influence : Reduced deformation and damage to the workpiece
- High-quality coating : High adhesion and uniform coating, low distortion and dilution
- High-speed, high-precision coating
- Can also be applied to complex shapes
- Areas of application
- Automotive industry, parts machining
- Aerospace industry, high strength parts machining
- Petroleum/marine equipment, high load machine parts, power generation equipment machining
- High performance industrial metals, mold coating, maintenance, life extension
- Key variables
- Powder feed rate, laser power, track spacing, scan path, cooling rate